Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is described as the representation of generalized human cognitive abilities in software so that, when faced with an unfamiliar task, the AGI system can find a solution. In other words, it's the ability of AI to learn in the same fashion as humans.
It can also be referred to as strong AI, full AI, or general intelligent action. However, some academic sources reserve the term "strong AI" for computer programs that experience sentience or consciousness. These definitions can vary as experts from different fields define human intelligence from different perspectives. Computer scientists, for example, often define human intelligence as being able to achieve goals. Psychologists, on the other hand, define general intelligence in terms of adaptability or survival.

Compared to strong AI, weak or narrow AI is not intended to have general cognitive abilities, meaning they are programs designed to solve only one problem and therefore do not experience consciousness. Examples include autonomous vehicles and IBM's Watson supercomputer. That said, AGI in computer science is posed as an intelligent system with comprehensive or complete knowledge and cognitive computing capabilities.
As it stands, no actual AGI systems currently exist and remain the stuff of science fiction. The performance of these systems is indistinguishable from that of a human, at least that's the long-term goal; however, the intellectual capacities of AGI could exceed human capacities because of its ability to access and process large data sets at incredible speeds compared to the human mind.
Today, AI is capable of executing a variety of tasks, including displaying personalized recommendations based on previous online searches. It can also identify different objects for obstacle avoidance with self-driving vehicles, identify cancerous cells during medical exams, and act as the nerve center for home automation. Moreover, it can help locate potentially habitable planets, be used as smart assistants, be tasked with security and more.
Of course, AGI looks to exceed those capabilities by far, and some scientists are worried it will lead to a dystopian future. Stephen Hawking warned against its development as it would view us as a potential threat and act accordingly, while Elon Musk stated that sentient AI would be more dangerous than nuclear war.
Fears aside, most scientists agree true AGI is decades, if not centuries, from being created and must adhere to a set of criteria (that's ever-evolving) before it can be realized. These include the ability to reason, use strategy, solve puzzles, and make judgments under uncertainty. It must also represent knowledge, including common sense, and be able to plan, learn and communicate in natural language. Going further, AGI must also be able to sense (see, hear, etc.) and output the ability to act, such as moving objects and changing locations to explore. With these in mind, how far along are we, and who is working towards the goal of creating Artificial General Intelligence?
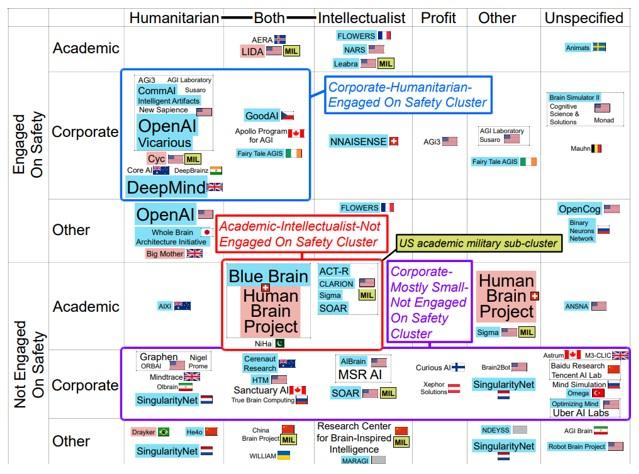
According to a 2020 survey from the Global Catastrophic Risk Institute (GCRI), 72 identified AGI R&D projects are currently being undertaken by academic institutions, corporations and various government entities. The survey suggests that the projects tend to be smaller, more geographically diverse, less open-source, less focused on academic goals, more focused on humanitarian goals, and more concentrated in private corporations compared to projects in 2017. The comparison also shows there has been a decrease in academic projects, an increase in corporation projects, an increase in projects focused on humanitarian goals, a decrease in projects with military connections, and a decrease in projects based in the US.
Governments and nonprofits play relatively minor roles in AGI R&D, including military projects that are centered on basic research only. That said, current projects are seemingly more diverse, and are characterized using three criteria, including corporate projects that are active on AGI safety with end goals that would benefit humanity. It also includes academic projects that are not active on AGI safety and focus on the advancement of knowledge, and small private corporations that are not active on AGI safety and provide a range of different goals.
Some of the more notable players conducting AGI projects include Carnegie Mellon University with its ACT-R, which looks to establish a general cognitive architecture based on fundamental cognitive and perceptual operations that enable the human mind. The project can be described as a way of specifying how the brain itself is organized in a way that enables individual processing modules to produce cognition.
Microsoft Research AI is another leading entity pushing the AGI boundaries and has undertaken a slew of research projects, including creating a data set to combat discrimination for machine-learning models. The company is also looking into advancing ethical AI, developing a responsible AI standard and developing AI strategy and assessments to establish an outline that focuses on the betterment of humanity.
Another interesting project venture comes from the man who created the popular video game series Commander Keen and the widely recognized Doom. John Carmack's latest startup, Keen Technologies, is an AGI advancement venture that's already gained $20 million in a financing round from former GitHub CEO Nat Friedman and Cue founder Daniel Gross. Carmack is in the optimist group regarding AGI and feels that it could benefit humanity and eventually lead to the creation of an AI mind that behaves like a human, which could serve as a universal remote worker.
So, what is the future of AGI? Most experts are skeptical that AGI will ever come to fruition, while others speculate that the desire to even create a synthetic intelligence on par with humans will fade away over time. Others are pursuing its advancement to benefit humanity as a whole.
However, even now, scientists are still in the planning stage of AGI development, with minimal advancements expected in the coming decades. That said, scientists have grappled with the creation of life-changing technologies throughout time and whether or not they would advance society or contribute to its destruction. This notion was pondered before the automobile was introduced, when AC current was being developed and when the atomic bomb was just an idea.
Will the creation of Artificial General Intelligence follow in those footsteps? It's anybody's guess.
RELATED: Robot ethics and sustainability tech discussed at Sensors Converge