Choosing a suitable IoT platform is arguably the most crucial step in building an IoT system. Most parties building an IoT ecosystem opt for an IoT platform due to its inevitable benefits: IoT platforms make provision for global real-time connection and management of many devices. They simplify the process of adding new devices to the network, configuring them, and updating their settings remotely. IoT platforms also collect data and have tools for analysis of the same. This approach is especially crucial in today’s market space as there is a surge in demand for integration of machine learning and AI for analysis of data collected by IoT devices.
The prerequisite data formats enabled by these IoT platforms simplify the initial hurdles in conducting analytics. They also have scope for customization and integration of multiple IoT systems, if necessary. IoT platforms often provide APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow integration with other enterprise systems, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) or CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems. APIs make the process of customization more efficient and reliable.
Innovation in IoT platform development
The larger body of IoT platform providers have shifted and adhered to an industry-driven approach to make advancements. Traditionally, IoT platforms were often developed with a more proprietary or vendor-specific mindset, focusing on individual product offerings and capabilities. However, now we can witness efforts to further develop IoT platforms in isolation while also understanding and addressing specific use cases prevalent in target industries. This has been particularly evident in the launches associated with Edge IoT and AIoT–major branches of technological advancements in IoT.
In one example, Advantech announced a series of new generation edge computing and AI platforms integrated with Edge AI SDK, EdgeSync 360, DeviceOn AIoT device management, and IoT Security software solutions, partnering with several global players including Intel, AMD, NVIDIA, Arm, and others.M.C. Chiang, vice president of Advantech's Service-IoT Group hopes that this will hasten the deployment of AIoT applications across healthcare, retail/hospitality, and public services/logistics/fleet management, and mobility. Tapping into these industries calls for addressing the prevalent challenges of IoT technologies, particularly security.
Security in IoT is a pervasive concern since each connective device is a potential entry point for invasion. These devices are also of diverse types and pose challenges in implementing standardized security measures. Inadequate authentication mechanisms, coupled with the vast attack surface, make unauthorized access and data manipulation more likely. The handling of sensitive data and the prevalence of outdated firmware further contribute to security vulnerabilities which seriously could hedge against the employment of IoT. Emphasizing security of IoT systems, up and coming companies like Armis Security, Asimily, Claroty and others are leveraging AI and ML driven platforms into sectors such as medical and industrial IoT. Medical IoT devices are often connected to monitor patients' health, administer treatments, or collect sensitive health data. Ensuring the security of these devices is paramount to safeguard patient safety and privacy. Unauthorized access or manipulation of medical IoT devices could have severe consequences, impacting the well-being of patients and violating their privacy rights.
Earlier in March 2023, Viakoo, a company in IoT/OT vulnerability remediation, announced a partnership with Presidio, a global digital services and solutions provider, to deliver comprehensive physical security to IoT systems. Viakoo’s Viakoo Action platform analyzes the very surface of cyber-attacks in IoT systems, which when supplemented by Presidio’s IoT cybersecurity solutions might be capable of a next generation IoT security framework. Viakoo Action's analysis of cyber-attacks coupled with Presidio's real-time incident response capabilities and in the event of a detected threat, the integrated security framework, can trigger immediate responses, such as isolating compromised devices, blocking malicious network traffic, or initiating remediation actions. This real-time response capability is crucial for minimizing the impact of cyber-attacks on IoT systems.
Big player engagements in IoT platforms
Meanwhile, the IoT extensions of big-name cloud computing platforms like Amazon Web Services IoT Core, Microsoft Azure IoT, Oracle IoT Cloud Services, among others, were popular choices amongst users. They were preferred over others for their low entry barrier and scope for connectivity for a larger number of devices in the network over their competitors. With user-friendly interfaces, comprehensive documentation, and reliable support systems, organizations and developers can easily initiate their large IoT projects without facing complex onboarding processes or steep learning curves.
2023 marked the release of newer advancements brought by the big players: Microsoft announced Azure IoT which assists in transfer of useful data to cloud services like Microsoft Fabric; AWS added multiple extensions to its IoT Core like AWS IoT FleetWise vision system data and AWS IoT SiteWise Edge on Siemens Industrial Edge B2B marketplace as well as a new open-source, no-code IoT dashboard application, aimed at allowing users to visualize and interact with data from its AWS IoT SiteWise service. Such efforts have been a response to the evolving landscape of emerging technologies and the accompanying challenges in integrating these advancements into IoT frameworks.
Adding analytics to IoT platforms
Akin to the Viakoo-Presidio partnership where analytics solutions were handy in overcoming security challenges in IoT, utilizing analytic tools for IoT systems in platforms is becoming more common. A classic example was the launch of Microsoft Fabric which when integrated into the Azure IoT cloud could be engaged in complex IoT projects for industries and enterprises. AI-driven analytics can identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or areas for improvement within an industrial or enterprise setting. These analytics contribute to increased operational efficiency, reduced downtime, and improved resource utilization. Hence, the combination of Microsoft Fabric and Azure IoT allows for the optimization of operational processes.
2023 also witnessed ABB (ASEA Brown Boveri), a global leader specializing in robotics, automation, and power technologies announced its investments in Pratexo to “deploy edge-based networks and solution architectures that provide real time insights, with the added benefits of reduced cloud data transfer volumes, improved data privacy and security, and the ability to run even when not connected to the internet.” Supplementing IoT networks with edge analytic capabilities is only a recent trend but with subsumed benefits: it offers a decentralized approach to data processing and hence enhances dynamic real-time analysis of network operating leading to increased efficiency of the IoT system. It also has the potential to resolve the data overload challenges that larger IoT systems pose to their developers and hence contribute to an elevated scalability. Even so, edge analytics was meagerly deployed in IoT in 2023 compared to the limelight it can be expected to receive in upcoming years.
The IoT observability challenge and interoperability
Edge analytics, AI and ML tools additions in IoT platforms enable developers to upscale IoT systems, but it has also made these systems more complex. Devices connected to the network are now more diverse with different protocols governing communication. Not only that, but the real-time data also transmitted by the huge pool of IoT devices is only increasing day by day. Monitoring and collecting data from this heterogeneous environment require versatile tools capable of handling diverse data formats and communication standards.
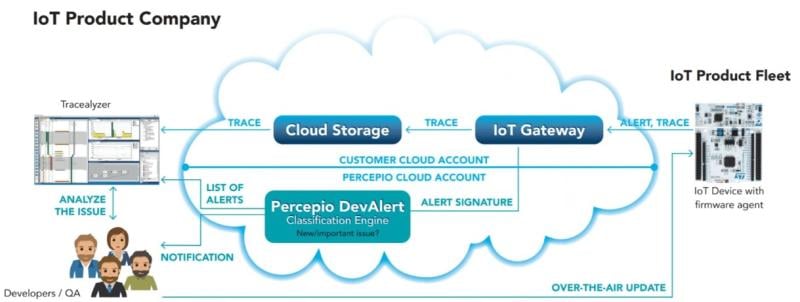
Referred to as IoT observability tools, these in the present day have their roots in the cloud computing space where they were “motivated by the complexity of debugging distributed systems and the adoption in embedded IoT/Edge devices is increasing for similar reasons,” explained Dr. Johan Kraft, CTO and founder of Percepio. “With increasing code size and system complexity in edge/IoT devices, you get higher deployment risks from bugs and vulnerabilities. Device developers need observability to ensure that issues are detected as early as possible…Observability means better data for improving the products, via OTA updates, and issues detected by observability can be resolved much faster by deploying an OTA update in the field. Moreover, observability allows for monitoring OTA deployments to ensure new issues are not introduced.” Percepio’s next-gen cloud-based observability tool DevAlert 2.0 typically employed in aerospace applications also has IoT applications. DevAlert 2.0 also addresses the data privacy challenges in cloud computing as well as IoT systems.With this tool, device developers can provide their own private storage for sensitive device data.
Another instance of the capabilities of observability tools is Assert.ai, which was acquired by Grafana Labs in 2023. “Assert helps us quickly correlate problems in the cluster and surfaces previously unknown, lingering issues,” said Gabriel Creti, engineering manager and technical lead. “Assert also offloads toil from our operations teams. By providing pre-made alerting rules and dashboards, it streamlines the painful job of maintaining them. It has always been a plus that the Assert UI embeds directly into Grafana.” Such an observability tool could potentially open gates to much more efficient cloud platforms and consequently IoT systems.
Inclusion of AI/ML furthers the cause of IoT in simplifying lives. IoT platforms often bridge the gap between other emerging technologies and IoT. Hence, furthering the advancements of IoT is not only contingent on technological leaps within and outside the IoT but also in this ‘bridge’ of integration. Development of reliable interoperability between two radically different IoT systems was a primary focus in 2023. CES2023 saw a diverse portfolio of announcements relating to smart home appliances and IoT pertaining to the Matter standardizations. In fact, Connectivity Standards Alliance announced the release of Matter 1.1 in May 2023. While the year did not witness a lot of leaps in Matter integration in IoT platforms, the latter can be expected soon.
Saumitra Jagdale is a technical writer with expertise in IoT, edge AI, embedded systems and electronics hardware.